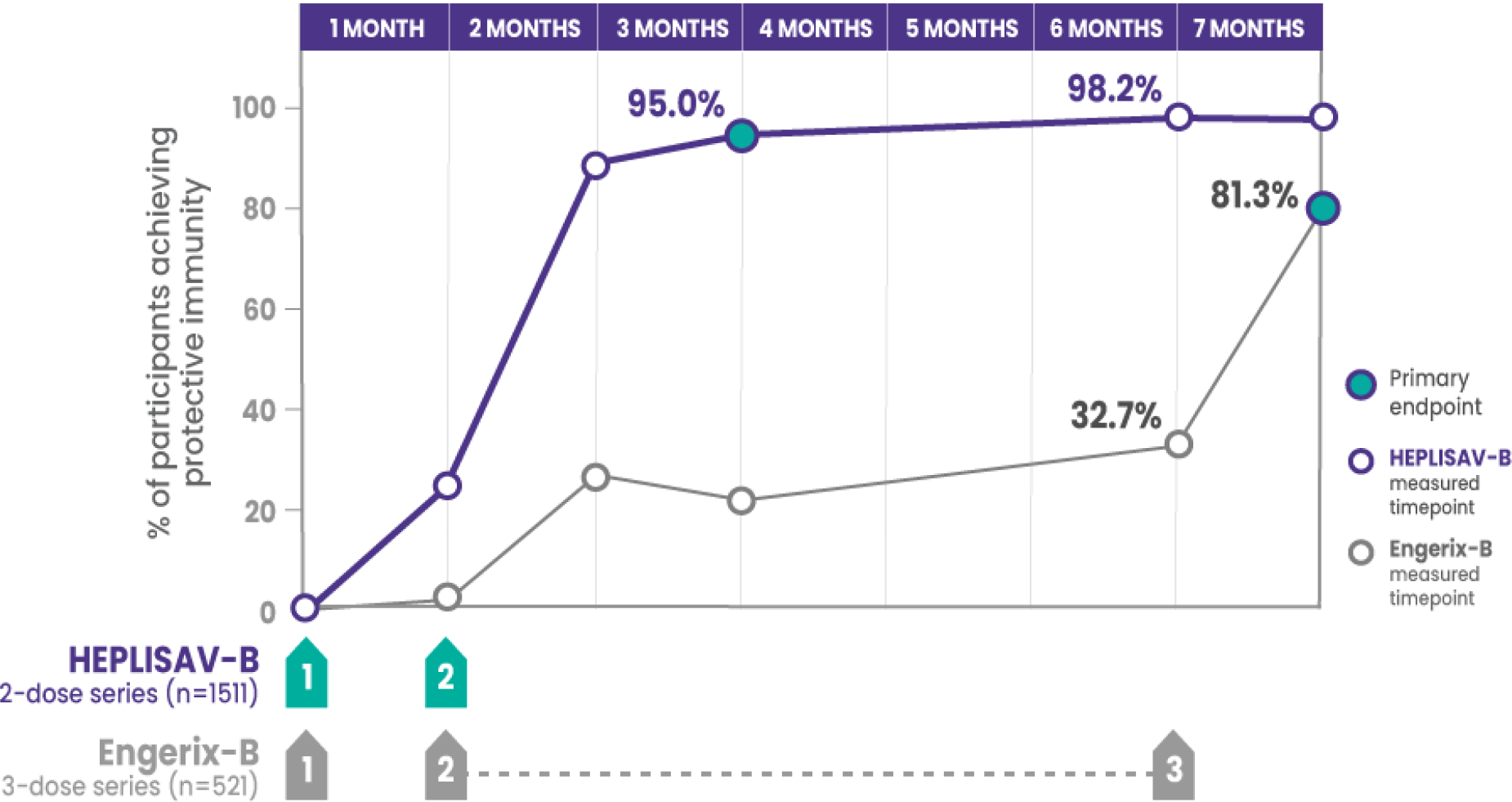
*Compared to 81.3% who received 3 doses of Engerix‑B.
†Protective immunity defined as antibody concentration ≥10 mIU/mL.
CI=confidence interval; SPRs=seroprotection rates
Statistically significantly higher rates of protection with HEPLISAV‑B vs Engerix‑B at every timepoint in adults aged 40–70 years
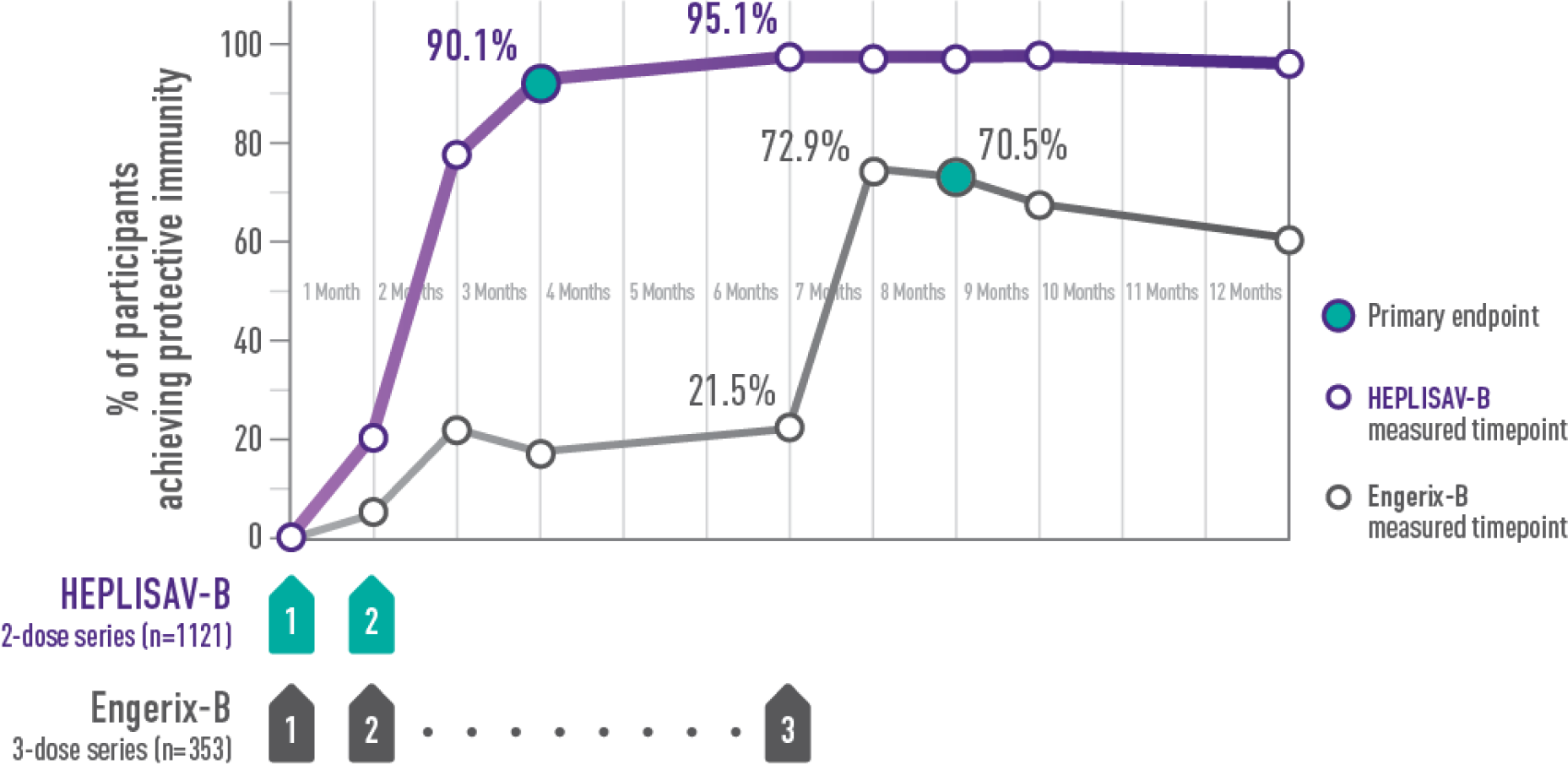
†Protective immunity defined as antibody concentration ≥10 mIU/mL.
ADULTS ACHIEVING PROTECTIVE IMMUNITY1,2
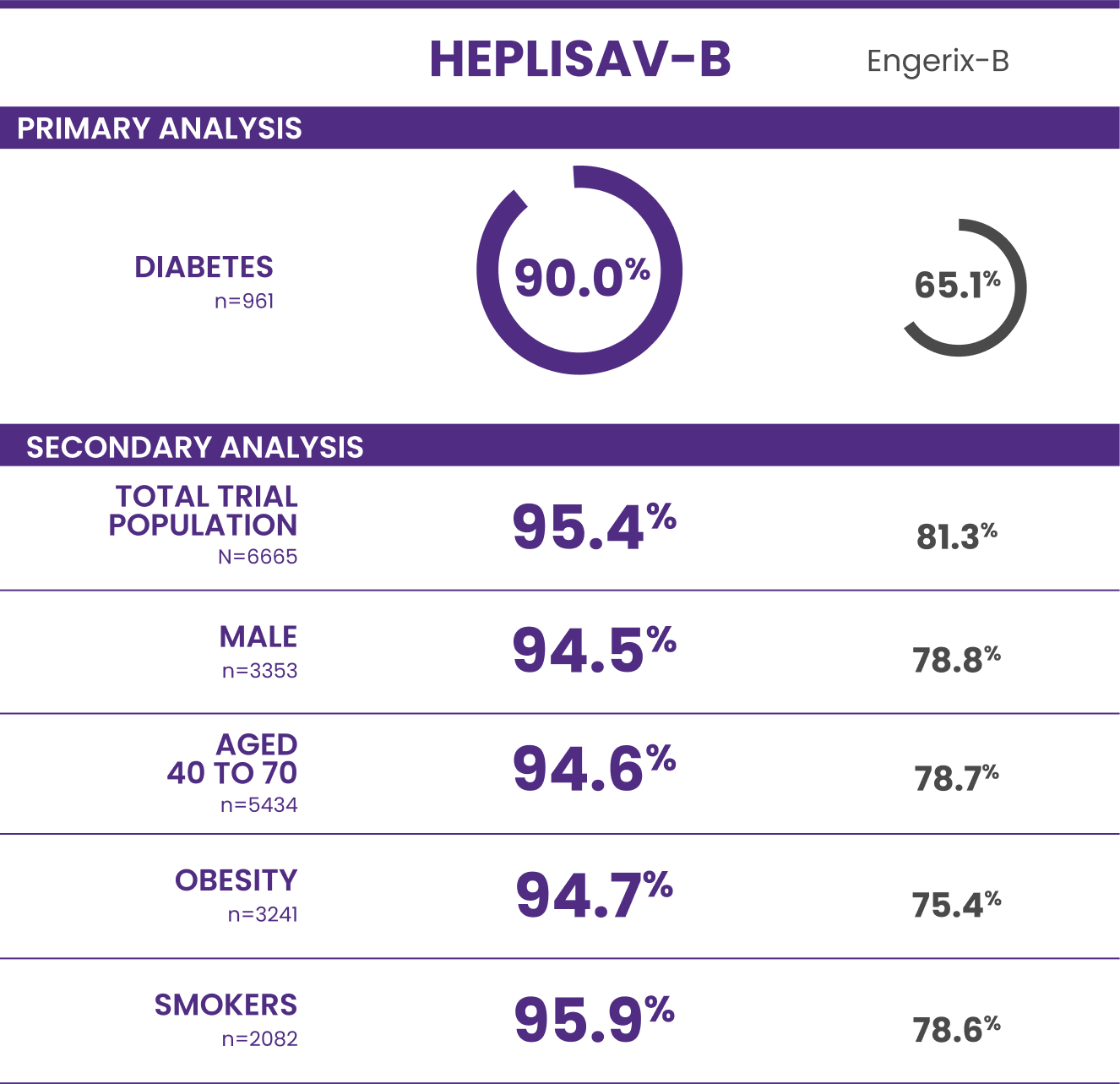
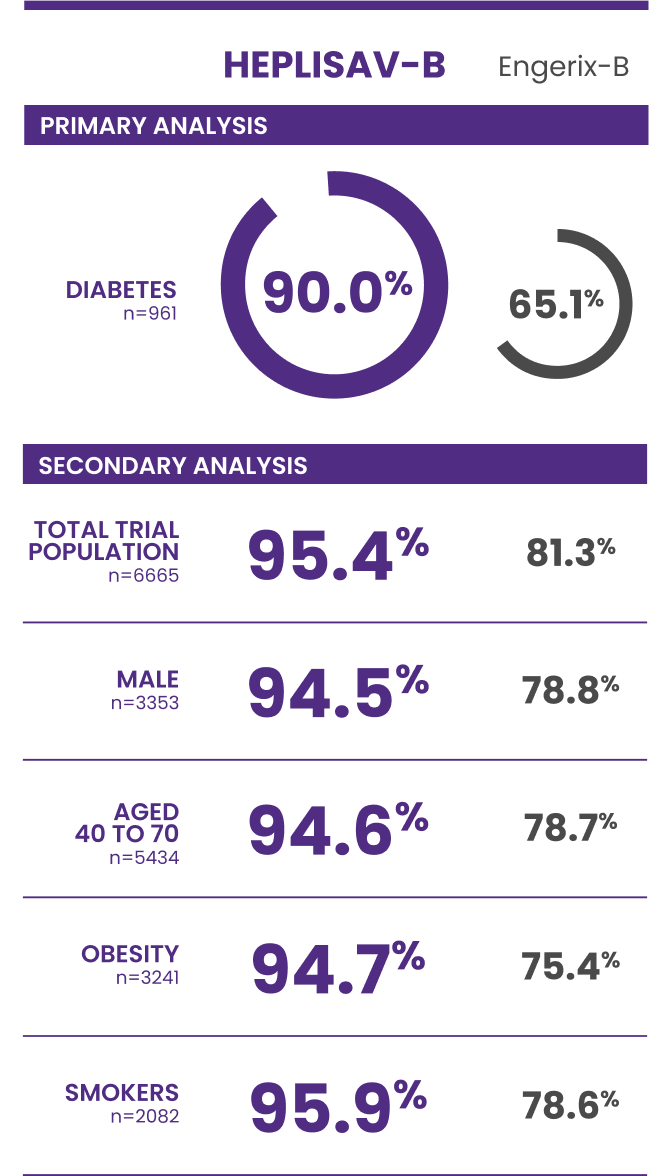
Trial 3 study design: A clinical trial in adults aged 18 to 70 years who received HEPLISAV‑B (n=4376) or Engerix‑B (n=2289).
†Protective immunity defined as antibody concentration ≥10 mIU/mL.
This site uses cookies to improve your experience. By continuing to use this website you are agreeing to our Cookie Policy.
INDICATION
HEPLISAV‑B is indicated for prevention of infection caused by all known subtypes of hepatitis B virus in adults 18 years of age and older.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Do not administer HEPLISAV‑B to individuals with a history of severe allergic reaction (eg, anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of any hepatitis B vaccine or to any component of HEPLISAV‑B, including yeast.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Do not administer HEPLISAV‑B to individuals with a history of severe allergic reaction (eg, anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of any hepatitis B vaccine or to any component of HEPLISAV‑B, including yeast.
Appropriate medical treatment and supervision must be available to manage possible anaphylactic reactions following administration of HEPLISAV‑B.
Immunocompromised persons, including individuals receiving immunosuppressant therapy, may have a diminished immune response to HEPLISAV‑B.
Hepatitis B has a long incubation period. HEPLISAV‑B may not prevent hepatitis B infection in individuals who have an unrecognized hepatitis B infection at the time of vaccine administration.
The most common patient-reported adverse reactions reported within 7 days of vaccination were injection site pain (23%‑39%), fatigue (11%‑17%), and headache (8%‑17%).
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of HEPLISAV‑B in pregnant individuals. Available data, primarily in individuals who received one dose of HEPLISAV‑B in the 28 days prior to or during pregnancy, do not suggest an increased risk of major birth defects and miscarriage.
It is not known whether HEPLISAV‑B is excreted in human milk. Data are not available to assess the effects of HEPLISAV‑B on the breastfed infant or on milk production/excretion.
Vaccination with HEPLISAV‑B may not result in protection of all vaccine recipients.
ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT INFORMATION
HEPLISAV‑B does not treat liver diseases such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.1
Not all liver cancer is caused by the hepatitis B virus.3
Please see full Prescribing Information.
1. HEPLISAV‑B [package insert]. Emeryville, CA: Dynavax Technologies Corporation; 2024. 2. Data on file. Dynavax Technologies Corporation. FDA advisory committee briefing document: HEPLISAV‑B™ (Hepatitis B Vaccine [recombinant], adjuvanted). Presented at: Meeting of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee; July 28, 2017; Silver Spring, MD. 3. National Cancer Institute. Liver cancer causes, risk factors, and prevention. Last updated May 15, 2024. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/types/liver/what-is-liver-cancer/causes-risk-factors